AI Middleware for Freight Operations: Connecting Emails, Documents, and Systems
In the world of logistics, a single shipment can spark fifty emails, a stack of PDFs, and updates across multiple systems. While the digital world moves at lightning speed, freight still moves at the speed of an attachment being downloaded. Hence, staying efficient, error-free, and adaptive to rapid change is no longer optional. AI Middleware is the bridge over this digital chasm. It isn’t just a “software upgrade”—it is the central nervous system for the modern supply chain.
This transformational trend goes far beyond basic automation. It represents the foundation of a connected digital freight ecosystem, where data flows continuously between unstructured sources such as emails and PDFs, and core operational platforms like Transportation Management Systems (TMS), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems. As freight networks become more complex and global, AI-powered middleware is quickly becoming a strategic necessity rather than a technological upgrade.
Why Freight Operations Need AI Middleware
Freight operations are inherently document-driven. Bills of lading, commercial invoices, customs declarations, packing lists, rate sheets, and high-volume email communications form the backbone of daily logistics activity. Much of this information exists in unstructured or semi-structured formats that require interpretation, validation, and action.
Key Challenges in Traditional Freight Workflows
Email overload: Freight professionals often spend hours each day managing inbound emails containing shipment updates, rate requests, carrier confirmations, and exception notices. Critical information is buried in long threads and attachments, increasing the risk of missed actions or delays.
Manual data entry: Extracting structured data from invoices, packing lists, or carrier documents is still heavily manual. This slows operations, introduces human error, and limits scalability during peak volumes.
Siloed systems: TMS, warehouse systems, pricing engines, finance platforms, and CRMs often operate independently. Teams are forced to rekey information across systems, creating inconsistencies and reducing real-time visibility.
Compliance risk: Documentation errors, missing regulatory details, or mismatched data can lead to shipment delays, fines, or customs holds—especially in cross-border freight.
These challenges inflate operating costs, slow turnaround times, and reduce visibility across the supply chain. AI middleware addresses these pain points by connecting fragmented parts of the freight workflow with intelligent automation — reducing manual workload and creating a unified, digital workstream across systems.
What is AI Middleware in Freight Operations?
At its core, AI middleware for freight operations is software that sits between unstructured data sources — such as emails, scanned PDFs, and documents — and structured enterprise systems like TMS, ERP, and CRM platforms. It ingests, interprets, and orchestrates data flow using machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and intelligent automation. It does not replace legacy systems; rather, it integrates and enhances them by enabling them to exchange meaningful data automatically.
Core Functions of AI Middleware
- Email Parsing & Communication Automation
Automatically scans inbound emails and attachments, extracting key shipment details, rate requests, or carrier replies and instructions.
Classifies messages and routes them to the appropriate workflow or system, eliminating manual inbox monitoring.
- Document Intelligence & Digital Extraction
Uses NLP and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to read complex freight documents, such as bills of lading, packing lists, invoices and custom forms.
Converts unstructured information into structured data fields — like shipment IDs, SKUs, weights, dates, and charges — that downstream systems can ingest.
- System Connectivity & API Integration
Serves as the middleware layer connecting disparate systems via APIs or connectors, keeping data synchronized in real time across TMS, ERP, CRM, and compliance platforms.
Triggers actions in connected systems based on extracted insights — such as creating a shipment record, updating a rate table, or generating a compliance alert.
- Exception Detection & Quality Control
Flags inconsistencies like mismatched weights between invoice and packing lists, or rate discrepancies across carriers.
Provides built-in validation to improve accuracy and reduce freight operation errors.
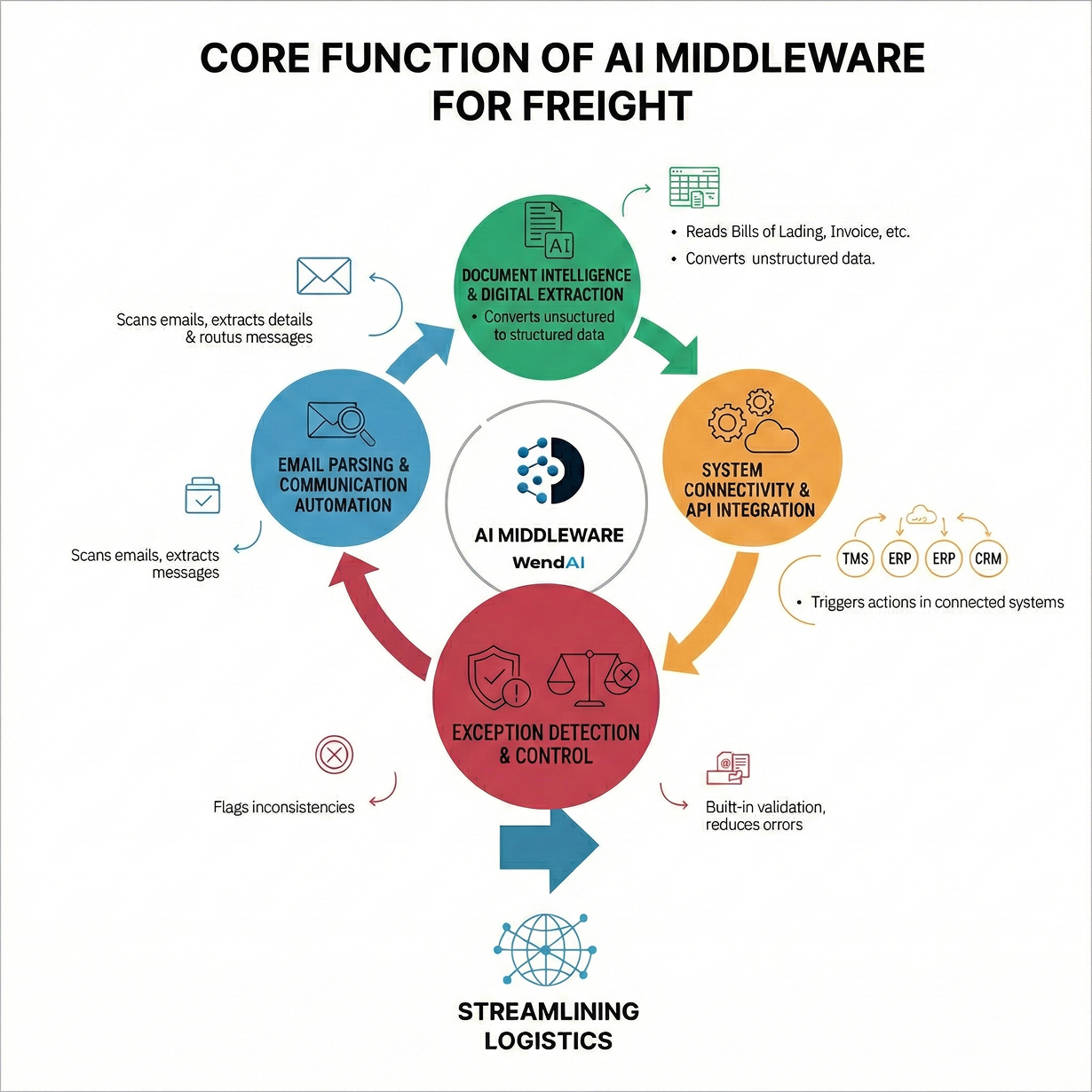
These capabilities make AI middleware more than a simple workflow tool; it becomes the data backbone of freight operations, enabling continuous, automated data flow across every functional area of the business.
Latest Market Trends
The freight industry is rapidly embracing AI middleware as part of a broader digital transformation. Several cutting-edge trends have emerged that point to how this functional capability is evolving:
- From Rule-Based Automation to AI-Driven Intelligence
Early automation solutions relied on static rules and rigid templates — effective only for standardized formats. Today, AI-powered middleware uses machine learning and NLP to handle a wide variety of document types and formats, including scanned images, multilingual emails, and non-standard carrier attachments. It can adapt and learn from new patterns over time, reducing the need for manual configuration.
- Breaking Free from EDI Dependency
Traditional Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) systems require strict formatting and partnership agreements. However, AI middleware can interpret freight data directly from emails and documents, eliminating much of the upfront development and maintenance required for EDI connections while expanding connectivity to smaller carriers that lack formal EDI capabilities.
- Intelligent Email Triage & Communication
Advanced systems now classify and respond to freight emails using NLP, extracting actionable instructions and integrating them into operations. This shift reduces time spent on routine communication and allows teams to focus on high-value decision-making.
- Enhanced Compliance & Regulatory Support
AI middleware doesn’t just extract data — it can also enforce compliance logic, cross-checking tariff codes, HS classifications, customs requirements, or license conditions before forwarding shipments. This capability helps reduce costly delays and improve international freight clearance.
- Increased Adoption Across Freight Forwarders and Brokers
Recent industry reports show that a growing share of freight companies are adopting AI solutions for automation and workflow optimization. In fact, a significant percentage of freight operators now report improvements in cargo tracking, documentation automation, and operational resilience due to AI investments.
Benefits for Freight Operations
AI middleware brings measurable value to freight operations in multiple dimensions:
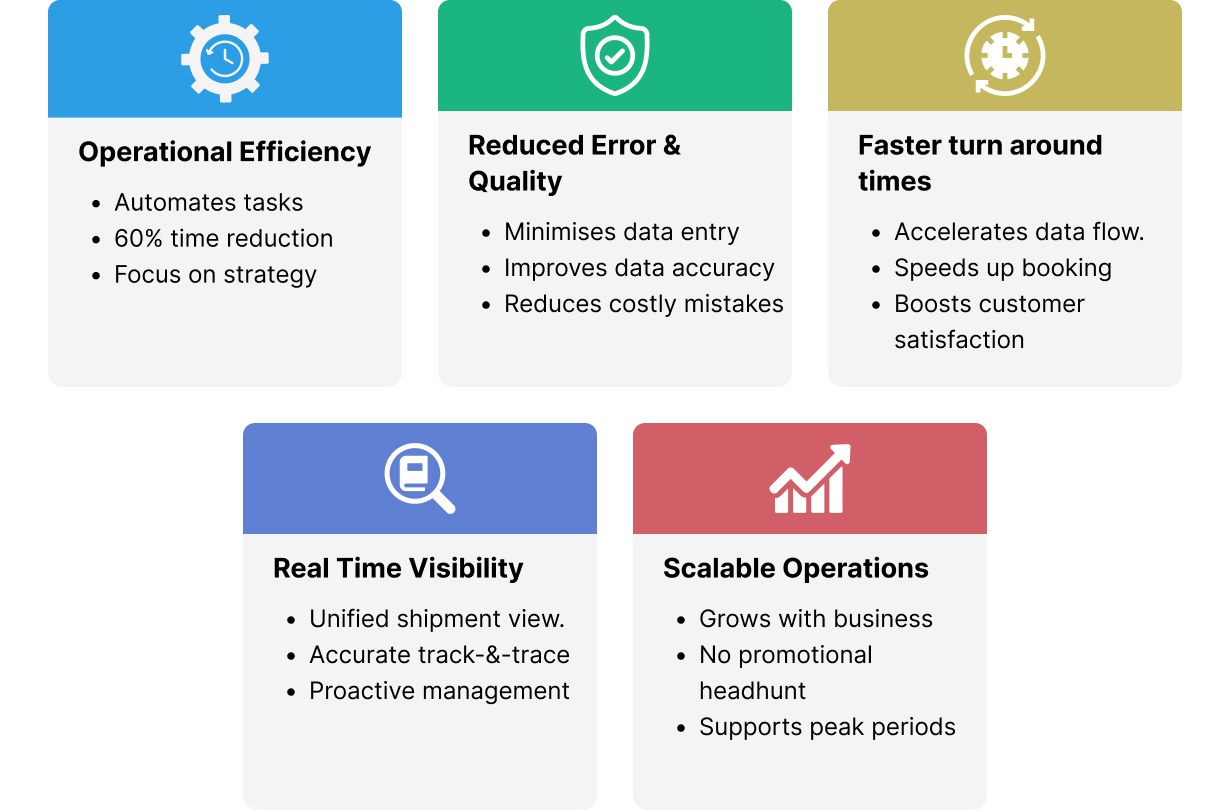
The Future of Connected Freight Workflows
While today’s AI middleware focuses on automation and integration, the future points toward a fundamental shift in how freight operations function at an industry level.
- Middleware as the Freight Operating Layer
Connected freight workflows will evolve into a persistent operational layer that continuously monitors, interprets, and adjusts freight activity. Rather than reacting to events, systems will operate in a constant state of alignment — reconciling what was planned, what is happening, and what is likely to happen next.
- Context-Aware Operations
Future middleware will not only process data but understand context — recognizing patterns across communications, documents, and historical outcomes. This enables smarter prioritization, early risk detection, and proactive intervention before disruptions escalate.
- Continuous Decision Loops
Planning and execution will merge into a single adaptive loop. Rate decisions, routing adjustments, compliance checks, and customer updates will continuously evolve as new information flows into the system.
- Probabilistic Freight Management
Instead of binary outcomes, connected workflows will operate on confidence levels and risk scoring — allowing teams to focus attention where uncertainty and impact are highest.
- Middleware as the Interface Between Companies
As freight ecosystems grow more interconnected, middleware will increasingly act as the primary interface between shippers, carriers, forwarders, and partners — enabling faster alignment, fewer disputes, and smoother collaboration.
- Documentation as an Active Control Mechanism
Freight documents will shift from passive records to dynamic operational inputs that influence pricing, routing, compliance, and prioritization in real time.
- Embedded Sustainability and Cost Intelligence
AI middleware will increasingly evaluate trade-offs between cost, service levels, and environmental impact — embedding sustainability optimization directly into freight execution.
To conclude…
AI middleware is redefining how freight operations connect emails, documents, and systems into a cohesive, intelligent workflow. What began as a tool for automation is rapidly becoming the connective tissue of modern logistics operations, enabling faster decisions, greater accuracy, and scalable growth.
As freight networks become more complex and global, organizations that invest in connected, AI-driven middleware will be better positioned to manage volatility, optimize costs, and deliver superior service.
The future of freight is not just automated — it is intelligently connected, and middleware sits at the center of that transformation.
